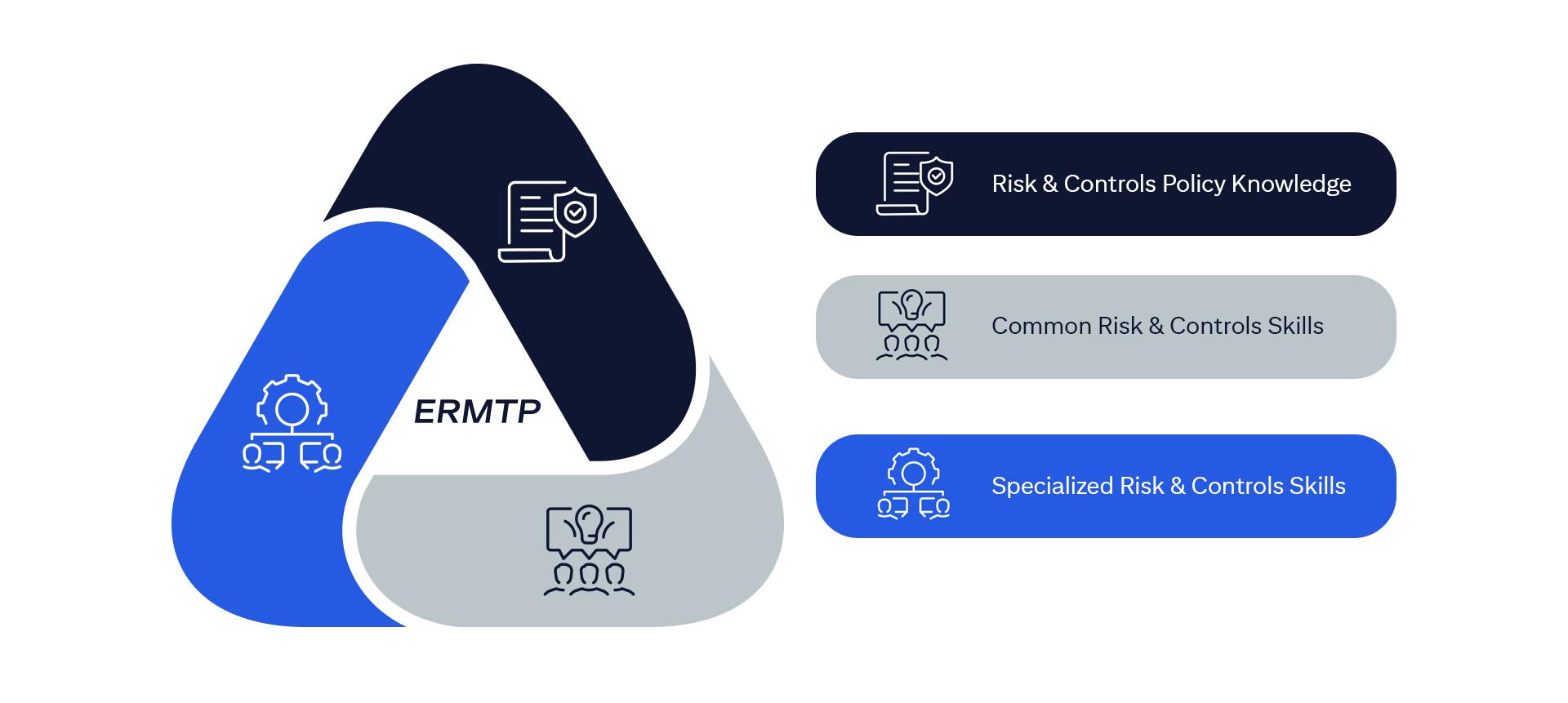
The ERMF establishes an overarching, integrated, and consistent approach to risk management firmwide.
This training will specifically focus on Market Trading Risk within Pillar 3 (Risk Management) of the ERMF.
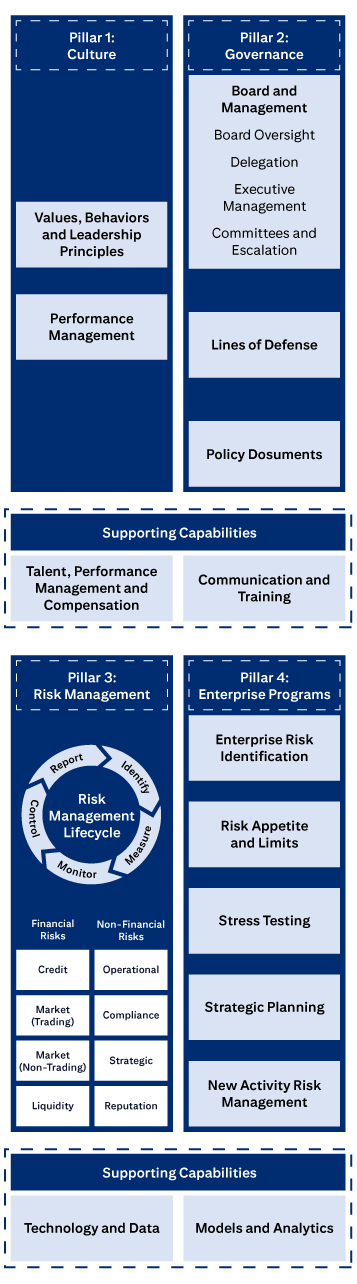
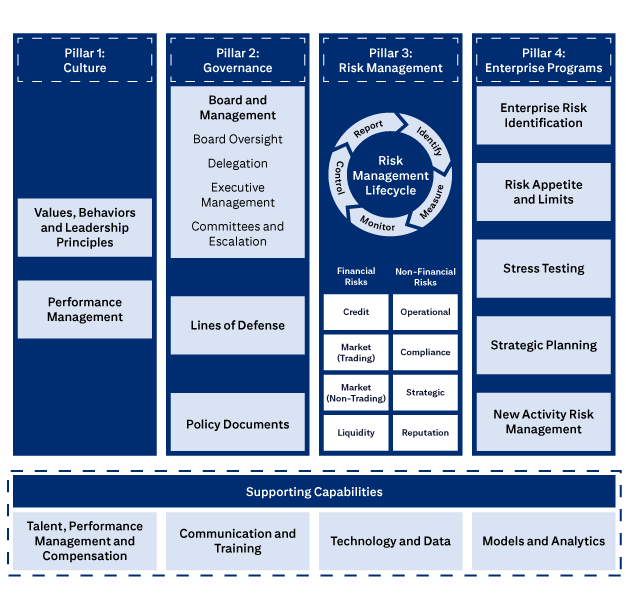

The four pillars of Citi’s ERM Framework.
Pillar 1: Culture includes Values, Behaviors and Leadership Principles, and Performance Management
Pillar 2: Governance includes Board and Management, Board Oversight, Delegation, Executive Management, Committees and Escalation, Lines of Defense, and Policies, Standards and Procedures.
Pillar 3: Risk Management covers the Risk Management Lifecycle (Identify, Measure, Monitor, Control, Report), Financial Risks (Credit, Market (Trading), Market (Non-Trading), Liquidity), and Non-Financial Risks (Operational, Compliance, Strategic, Reputation).
Pillar 4: Enterprise Programs covers Enterprise Risk Identification, Risk Appetite and Limits, Stress Testing, Strategic Planning, and New Activities Approval.
Supporting Capabilities are: Talent, Performance Management and Compensation; Communication and Training; Technology and Data; and Models and Analytics.



We use risk metrics outlined in regulatory guidelines, including Basel 2.5 and FRTB, to monitor market risk.
To proceed, select each Basel Pillar to learn more.



Key Metrics
Value at Risk (VaR), Incremental Risk Charge (IRC), Comprehensive Risk Measure (CRM)
Usage
Calculation of minimum capital requirements for market risk and credit risk in the trading book. Factor sensitivities are foundational inputs for VaR, IRC, and CRM calculations.
go to next button
Key Metrics
Stress Tests, Incremental Default Loss (IDL)
Usage
Assessment of a bank's overall risk profile, capital adequacy, and resilience to adverse economic conditions.
go to next button
Key Metrics
Disclosure of VaR, Stress Test Results, Capital Adequacy
Usage
Enhancing transparency and allowing market participants to assess a bank's financial health.
The following are all subtypes or enhancements of simulation-based VaR techniques.
To proceed, select each button to learn more about Value at Risk.





The legacy metric, but is still used to monitor risk and calculate risk capital.
go to next button
An advanced calculation that estimates potential losses using historical market data applied to the current portfolio.
go to next button
Approximates exposure using sensitivities to risk factors and their historical distributions.
go to next button
Revalues the entire portfolio under each historical scenario for accuracy.
go to next button
Uses full revaluation primarily, but falls back to a risk-based approach if full revaluation fails in a scenario.
Stress tests evaluate the impact of extreme but plausible market scenarios on the trading book's maximum losses under defined scenarios. The following categories are the purposes of stress testing at Citi.
To proceed, select each category to learn more.
Global Market Risk Stress Losses are monitored against Market Risk limits and against Capital-Based Stress Loss (CBSL) limits.
go to next button
Used in cases of emerging risks and/or unforeseen changes to the macro-economic environment to inform senior management of the potential impact of imminent or active risks using a quick and forward-looking assessment.
go to next button
Supports capital planning and business planning processes including, but not limited to, the Federal Reserve’s annual Comprehensive Capital Analysis and Review (CCAR) exercise, the Federal Reserve’s and Office of the Comptroller of the Currency’s Dodd-Frank Act Stress Testing (DFAST) exercise, and the quarterly Capital Adequacy Assessment.



While market risk management have its own internal tiering system (as per "Limit Categories"), Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) has implemented a standardized classification system for limits across the entire enterprise. This system is based on the maximum amount of stress loss and risk capital associated with the limits, categorizing them as follows:
Category B / C:
Category D:
To proceed, select each category to learn more.




Risk Metric Type: Firm-Wide
Citigroup and CBNA Limits:
Risk Appetite limits and thresholds, corresponding to Market Risk Tier 0 limits
Description of Risk Metrics in scope:
Risk Metrics whose limit breach may have a significant adverse impact on Citi’s ongoing ability to carry on business, meet client obligations, and/or comply with regulatory requirements.
go to next button
Risk Metric Type: Firm-Wide
Citigroup and CBNA Limits:
Enterprise risk limits and thresholds, corresponding to Market Risk Tier 0/1 limits
Description of Risk Metrics in scope:
Any other Citigroup or CBNA level Risk Metrics not already included in Category A
go to next button
Risk Metric Type: Sector-Level
Citigroup and CBNA Limits:
Risk category or major business risk limits and thresholds, corresponding to Market Risk Tier 2 limits
Description of Risk Metrics in scope:
Business Level and CBNA Legal Entity Level Risk Metrics, subject to the stress loss materiality threshold
Risk Metric Type: Sector-Level
Citigroup and CBNA Limits:
Operating risk limits and thresholds, corresponding to Market Risk Tier 2/3 limit
Description of Risk Metrics in scope:
All Tier 2 or 3 limits, subject to the stress loss materiality threshold
In this situation, what process should be followed?

Step 1:
The risk manager notifies the desk of the breach and requests a remediation plan.

Step 2:
The desk explains that the breach resulted from the recently executed trade and acknowledges that the affected limit was unintentionally omitted from the original request.

Step 3:
The risk manager classifies the breach as a true breach and assesses whether the limit can be subsequently increased.



The key components of the LCI Trade Pre-Trade Approval (PTA) process and the supporting T+1 controls are listed below.
These mechanisms ensure that LCI trades are properly identified, assessed, monitored, and escalated in line with Citi’s market risk governance framework.
To proceed, select each step to learn more.
At trade booking, the Trader flags a trade as a potential LCI and submits a Pre-Trade Approval (PTA) request to Market Risk. Market Risk estimates the 1-in-10 stress loss. Based on this, the request is escalated to appropriate Business and Risk approvers for a decision (approve, revise, reject). If approved, the trade must be executed within 30 calendar days.
go to next button
An automated system scans newly booked and amended trades daily against LCI criteria. A report is generated for Risk Managers on T+1. This information highlights flagged trades and any exceptions.
Market Risk reviews exceptions to determine if they are false positives or actual breaches (violations). Traders must report any known rule violations to Market Risk Managers.
go to next button
Desk Heads and Market Risk Managers receive automatic alerts for all T+1 violations via the supervisory alerting system.



This TB/BB classification has a direct impact on how positions are treated under the following Regulatory Capital requirements:
The TB/BB boundary is the primary factor that determines which set of Regulatory Capital rules applies and therefore drives the capital treatment of the positions.
To proceed, select each tab to learn more.
Positions that may require transfer out of the Trading Book are identified during the quarterly ex-post review process. Global Market Risk collaborates with Finance and the Business to assess and flag positions for potential transfer to the Non-Trading Book (NTB), also known as the Banking Book.
Transfers are considered when positions no longer meet Trading Book eligibility criteria. Common reasons include:
go to next button
A formal process must be followed for all TB-to-NTB transfers, which includes:
go to next button
Specific to Trading Book Covered exclusions, if Regulatory Capital changes from Market Risk to Wholesale Credit Risk, Credit Risk is responsible for determining whether the counterparty has an active credit relationship with Citi, or needs an appropriate risk rating for the Wholesale RWA process.
The following image shows a simple visual timeline that lays out the steps of transferring positions.

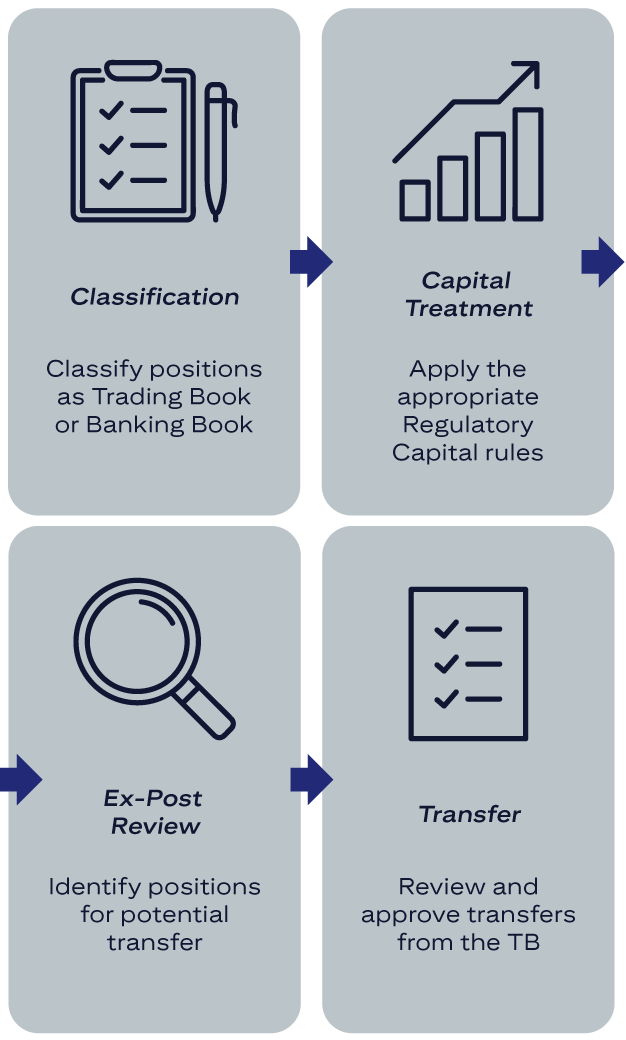
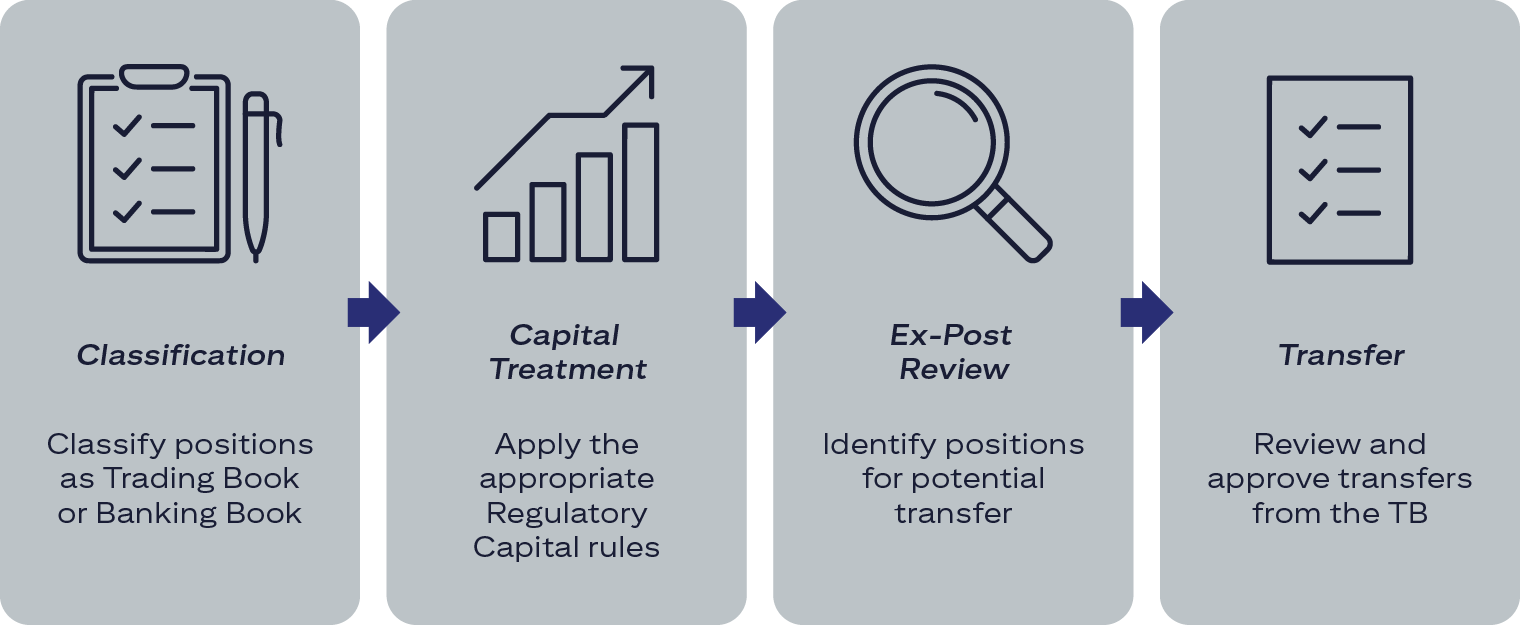
Classification: Classify positions as Trading Book or Banking Book. Capital Treatment: Apply the appropriate Regulatory Capital rules. Ex-Post Review: Identify positions for potential transfer. Transfer: Review and approve from the TB



Although GMR typically operates on the public side, in this instance, the Trader realizes that sharing full trade details—including the issuer identity—could potentially expose MNPI.
To proceed, select each category to learn what happens next.
The Trader pauses the discussion and contacts the Control Group for guidance.
go to next button
The Control Group reviews the context and approves a wall crossing for a specific GMR Risk Manager.
The Risk Manager receives formal wall-crossing notification, restricting their communications and trading activity on the impacted issuer.
go to next button
The wall-crossed GMR Risk Manager reviews the proposed transaction, conducts a stress loss analysis, and provides guidance back to the Trader and desk leadership.
Other GMR personnel remain on the public side and are not included in discussions or data access.



Unmanaged market risk can cause major losses to Citi’s capital and earnings, while effective risk management protects against adverse market shifts. Regulators mandate strong risk frameworks, and compliance helps Citi prevent penalties and preserve its reputation.
To proceed, select each Takeaway to learn more.
Trading Market Risk forms a significant component of Price Risk.
go to next button
Key Market Risk Metrics such as Value at Risk (VaR), Incremental Risk Charge (IRC), and Stress Testing are used to monitor and manage market risk.
go to next button
Citi’s Market Risk Limit Framework sets and reviews market risk limits at various organizational levels, including triggers and governance layers.
go to next button
The Large Complex Illiquid Trade Pre-Approval Process is used for identifying LCI trades, the steps in the pre-trade approval process.
Positions that may require transfer out of the Trading Book to the Banking Book are identified during the quarterly ex-post review process.
Transfers are considered when positions no longer meet Trading Book eligibility criteria. Common reasons include:
MNPI can only be shared under specific, approved circumstances. If you’ve received MNPI—whether intentionally or inadvertently—you must not trade on it.
Engaging in or facilitating trading based on MNPI is strictly prohibited.



What is the primary objective of Citi's Market Risk Limit Framework?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The Market Risk Limit Framework is designed to prevent excessive exposure to market risk and ensure financial stability.
The Market Risk Limit Framework is designed to prevent excessive exposure to market risk and ensure financial stability.
The Market Risk Limit Framework is designed to prevent excessive exposure to market risk and ensure financial stability.
That answer is correct.
The Market Risk Limit Framework is designed to prevent excessive exposure to market risk and ensure financial stability.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Market Risk Limit Framework section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Market Risk Limit Framework section.
Which of the following is NOT a Key Market Risk Metric?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
EBIT is a financial performance metric, not a market risk metric.
EBIT is a financial performance metric, not a market risk metric.
EBIT is a financial performance metric, not a market risk metric.
That answer is correct.
EBIT is a financial performance metric, not a market risk metric.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Price Risk and Market Risk section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Price Risk and Market Risk section.
Which layer of market risk limits are set at trading desk level?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
Tier 3 sets limits at the individual trading desk level.
Tier 3 sets limits at the individual trading desk level.
Tier 3 sets limits at the individual trading desk level.
That answer is correct.
Tier 3 sets limits at the individual trading desk level.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Market Risk Limit Framework section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Market Risk Limit Framework section.
What does wall crossing allow in a controlled environment?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
Wall crossing allows Material Non-Public Information (MNPI) to be shared with approved individuals for legitimate business needs.
Wall crossing allows Material Non-Public Information (MNPI) to be shared with approved individuals for legitimate business needs.
Wall crossing allows Material Non-Public Information (MNPI) to be shared with approved individuals for legitimate business needs.
That answer is correct.
Wall crossing allows Material Non-Public Information (MNPI) to be shared with approved individuals for legitimate business needs.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Handling MNPI and Information Barriers section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Handling MNPI and Information Barriers section.
Which one of the following processes describe the daily review of newly booked trades, performed on the business day following trade execution, to identify and assess potential Large Complex Illiquid (LCI) Pre-Trade Approval (PTA) violations based on defined thresholds, subsequently requiring review by Market Risk Managers to distinguish true violations from false positives?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The T+1 Detection Tool automates the review of trades against LCI thresholds defined in the strategic infrastructure.
The T+1 Detection Tool automates the review of trades against LCI thresholds defined in the strategic infrastructure.
The T+1 Detection Tool automates the review of trades against LCI thresholds defined in the strategic infrastructure.
That answer is correct.
The T+1 Detection Tool automates the review of trades against LCI thresholds defined in the strategic infrastructure.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Large Complex Illiquid Trades, Pre-Trade Approvals section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Large Complex Illiquid Trades, Pre-Trade Approvals section.
How is Stressed Value-at-Risk (SVaR) different than Value at Risk (VaR)?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
Breaches require immediate reporting and a formal analysis—even if they aren’t violations.
Breaches require immediate reporting and a formal analysis—even if they aren’t violations.
Breaches require immediate reporting and a formal analysis—even if they aren’t violations.
That answer is correct.
Breaches require immediate reporting and a formal analysis—even if they aren’t violations.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Market Risk Limit Framework section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Market Risk Limit Framework section.
Who signs off on Level 1 (Total Mark to Market Trading) key metrics in CRISP?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The Head of GMR is responsible for Level 1 sign-off.
The Head of GMR is responsible for Level 1 sign-off.
The Head of GMR is responsible for Level 1 sign-off.
That answer is correct.
The Head of GMR is responsible for Level 1 sign-off.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Price Risk and Market Risk section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Price Risk and Market Risk section.
When can a position be transferred from the Trading Book to the Banking Book?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
Transfers occur when positions no longer meet Trading Book eligibility, such as change in intent or liquidity.
Transfers occur when positions no longer meet Trading Book eligibility, such as change in intent or liquidity.
Transfers occur when positions no longer meet Trading Book eligibility, such as change in intent or liquidity.
That answer is correct.
Transfers occur when positions no longer meet Trading Book eligibility, such as change in intent or liquidity.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Trading Book/Banking Book Boundary section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Trading Book/Banking Book Boundary section.
What is the purpose of the CRISP platform?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
CRISP is used by Risk Managers to sign off on metrics like VaR, IRC, and stress loss.
CRISP is used by Risk Managers to sign off on metrics like VaR, IRC, and stress loss.
CRISP is used by Risk Managers to sign off on metrics like VaR, IRC, and stress loss.
That answer is correct.
CRISP is used by Risk Managers to sign off on metrics like VaR, IRC, and stress loss.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Price Risk and Market Risk section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Price Risk and Market Risk section.
Which one of these statements accurately describes the scope of Price Risk?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
Price Risk is equal to Trading Market Risk, plus the Financial Statement Reporting Risks associated with independent price verification and profit attribution analysis.
Price Risk is equivalent to Trading Market Risk in terms of quantity of risk.
It has an incremental scope that includes the economic exposure of non-trading products held in the trading business under Trading Market Risk.
Price Risk is equal to Trading Market Risk, plus the Financial Statement Reporting Risks associated with independent price verification and profit attribution analysis.
Price Risk is equivalent to Trading Market Risk in terms of quantity of risk.
It has an incremental scope that includes the economic exposure of non-trading products held in the trading business under Trading Market Risk.
Price Risk is equal to Trading Market Risk, plus the Financial Statement Reporting Risks associated with independent price verification and profit attribution analysis.
Price Risk is equivalent to Trading Market Risk in terms of quantity of risk.
It has an incremental scope that includes the economic exposure of non-trading products held in the trading business under Trading Market Risk.
That answer is correct.
Price Risk is equal to Trading Market Risk, plus the Financial Statement Reporting Risks associated with independent price verification and profit attribution analysis.
Price Risk is equivalent to Trading Market Risk in terms of quantity of risk.
It has an incremental scope that includes the economic exposure of non-trading products held in the trading business under Trading Market Risk.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Price Risk and Market Risk section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Price Risk and Market Risk section.








go to close menu button
go to close button