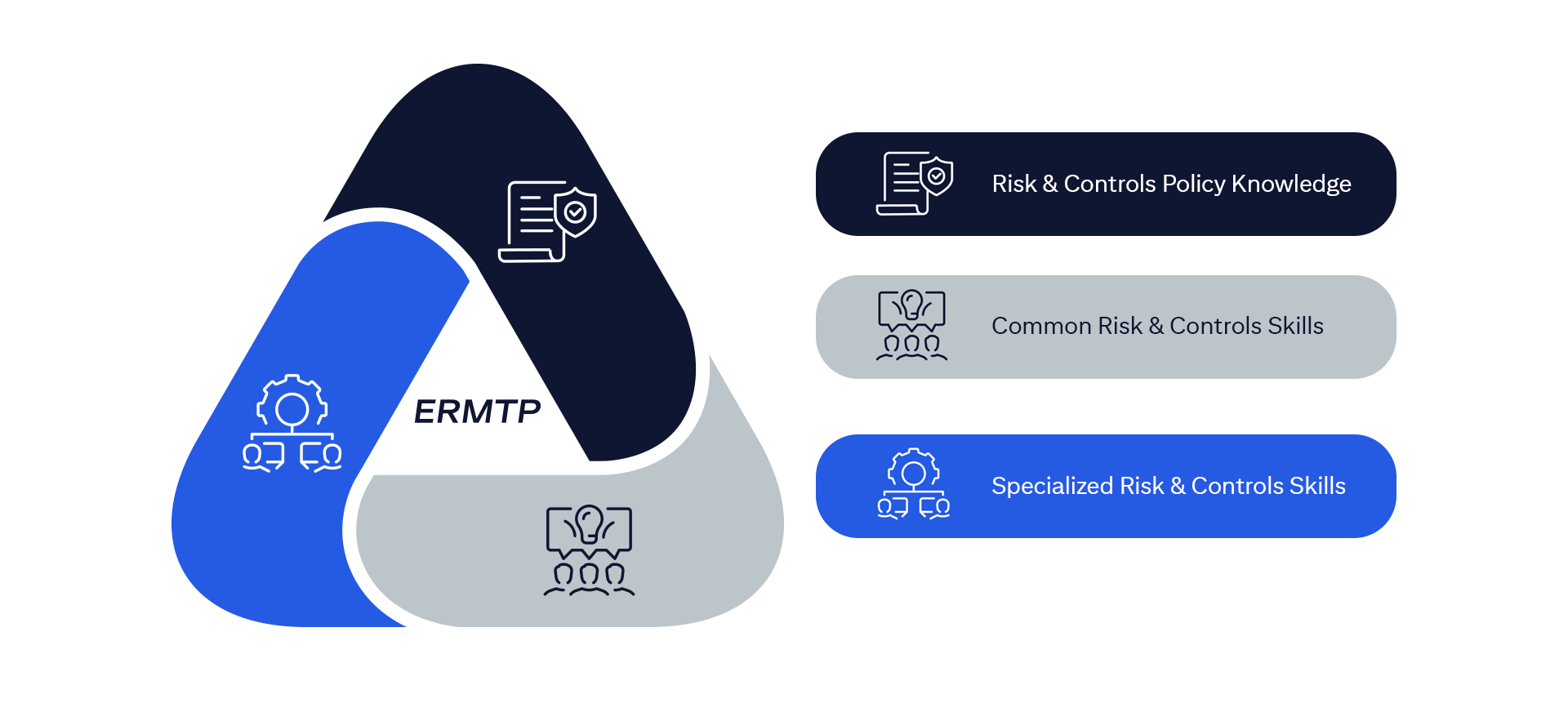
The ERMF establishes an overarching, integrated, and consistent approach to risk management firmwide.
This training will specifically focus on Market (Non-Trading) Risk within Pillar 3 (Risk Management) of the ERMF.
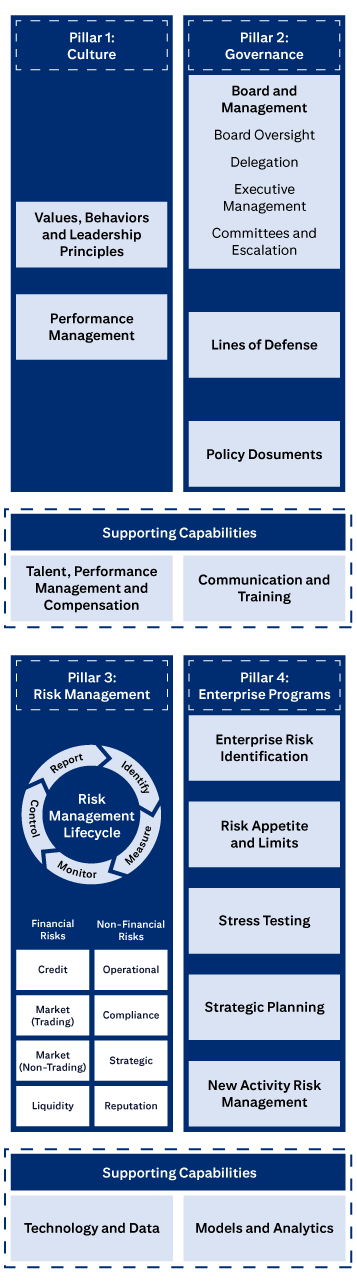
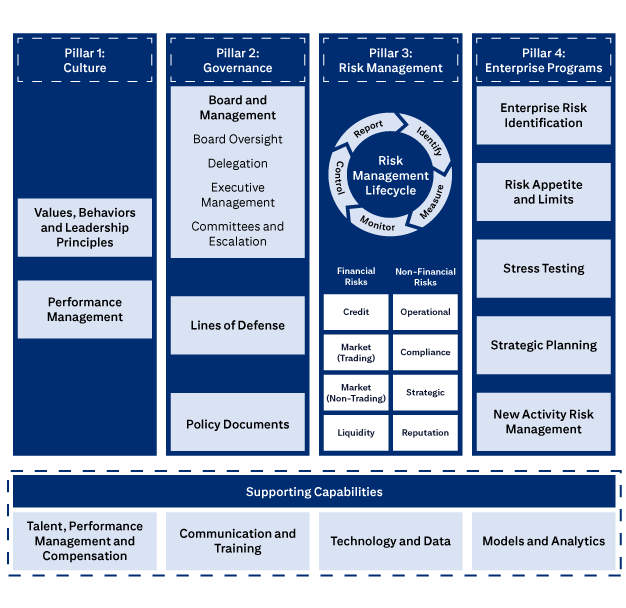

The four pillars of Citi’s ERM Framework.
Pillar 1: Culture includes Values, Behaviors and Leadership Principles, and Performance Management
Pillar 2: Governance includes Board and Management, Board Oversight, Delegation, Executive Management, Committees and Escalation, Lines of Defense, and Policies, Standards and Procedures.
Pillar 3: Risk Management covers the Risk Management Lifecycle (Identify, Measure, Monitor, Control, Report), Financial Risks (Credit, Market (Trading), Market (Non-Trading), Liquidity), and Non-Financial Risks (Operational, Compliance, Strategic, Reputation).
Pillar 4: Enterprise Programs covers Enterprise Risk Identification, Risk Appetite and Limits, Stress Testing, Strategic Planning, and New Activities Approval.
Supporting Capabilities are: Talent, Performance Management and Compensation; Communication and Training; Technology and Data; and Models and Analytics.









Non-Trading Market Risk (NTMR) Policy defines governance and escalation requirements for NTMR limits and MATs applicable to Citigroup, CBNA Consolidated, and other in-scope IRRBB Units. Governance and escalation requirements are determined based on the category of the limit/MAT.
Refer to the following sections in the policy/procedure documents for more information:
Non-Trading Market Risk Policy:
3.3: Non-Trading Market Risk Limits
Non-Trading Market Risk Procedure:
2.3: Non-Trading Market Risk Limits
To proceed, select each category to learn more.
NTMR limits and MATs must be established on Citi/CBNA regulatory and risk appetite metrics.
Category A limits and MATs are applicable to Citigroup and CBNA Consolidated.
go to next button
NTMR limits and MATs must be established on other Citi/CBNA material risk metrics.
Category B limits and MATs are applicable to Citigroup and CBNA Consolidated.
go to next button
NTMR limits and MATs must be established on material NTMR metrics (other than Citigroup/CBNA).
go to next button
These NTMR metrics are less material and may include MAT only and/or other risk metrics.
These metrics do not meet the criteria for Categories A-C.
Let’s review some examples that illustrate how Non-Trading Market Risk (NTMR) manages different types of limits to control non-trading market risks across various IRRBB Units. The specific limits, monitoring frequencies, and escalation procedures may vary depending on the materiality and complexity of the risks involved, as outlined in the NTMR Policy.
To proceed, select each example to learn more.
Consider Citi's Canadian branch, which might have an IRE limit of $100 million for a +200bps parallel shock to interest rates. This limit represents the maximum allowable decrease in net interest income due to such a rate change.
NTMR monitors this limit monthly, using ONYX. If the branch's IRE exceeds the limit, ONYX would automatically notify the branch treasurer and CBNA & LE Finance CRO via emails.
They would then collaborate on a remediation plan, which could involve adjusting the branch's balance sheet structure or hedging strategies. Similar limits and procedures would apply to EVS, which measures the impact of interest rate changes on the economic value of the branch's assets and liabilities.
go to next button
This limit aims to control the AFS DV01 risk exposure.
NTMR monitors this limit daily through the Treasury Risk Reporting processes. If the OCI AFS DV01 exposure approaches or exceeds the limit, NTMR would notify governance forums, including Citigroup ALCO.
Treasury would then need to propose risk remediation actions for AFS portfolio to bring OCI AFS DV01 exposure back within the established limit. This process involves reviews by NTMR and approvals by relevant committees.
go to next button
Citigroup OCI Capital at Risk limit monitors the potential impact of unrealized OCI losses on AFS securities under stress test scenarios. NTMR calibrates and monitors this limit based on balance sheet composition and operating plan.
If the OCI Capital at Risk stress loss approaches the limit or exceeds the MAT, NTMR would coordinate with 1st Line Treasury to remediate potential excesses of OCI Capital at Risk Limit/MAT.
go to next button
Imagine a scenario where Citi's Canadian operations have a notional FX limit of $10 billion CAD and a management action trigger (MAT) of $8 billion CAD. This limit/MAT is designed to restrict the unit's exposure to fluctuations in the CAD/USD exchange rate. NTMR monitors this exposure daily using a Consolidated Sovereign Issuer Report, which leverages limits/MATs stored in Limit Central/ONYX.
If the Canadian operations' notional FX exposure exceeds the $8 billion MAT, appropriate Treasury team is notified. Treasury will then draft and execute a remediation plan, which could involve reducing FX exposure through hedging or other strategies.
If the exposure exceeds $10 billion, it is recorded as a limit breach and communicated to the unit's treasurer and legal entity Finance CRO. Treasury takes steps to reduce their exposure to be under the approved limit.



Over the past few decades, global crises have caused sharp shifts in interest rates, exchange rates, and financial instrument prices. Banks operating outside the US are particularly vulnerable, as emerging markets are more volatile.
To proceed select each image to learn more.



For instance, the Asian crisis led to steep declines in many emerging currencies.
Banks holding assets in these currencies can face significant losses, something stress testing helps prepare for.
go to next button
Banks use both regulator-prescribed and internal scenarios to model potential negative outcomes.
The goal is to ensure they have enough resources to remain solvent and operational during market shocks.
These scenarios often draw from real crises, like the Asian and Global Financial Crises, forming part of Global Systemic and Business-Specific Stress Testing Programs.
go to next button
Stress testing reveals true exposure levels and potential losses. If well-hedged, the impact can be reduced.
This process helps assure clients, partners, and regulators that the bank is prepared for severe financial disruptions.
go to next button
In short, stress testing ensures that banks—especially large, systemically important ones like Citi—can withstand even the harshest economic shocks and continue operating securely.






What is the primary purpose of Citi's Non-Trading Market Risk (NTMR) Policy?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The primary purpose of Citi's NTMR Policy is to establish minimum requirements for identifying, measuring, monitoring, controlling, and reporting Non-Trading Market Risk, consistent with Citi’s risk appetite.
The primary purpose of Citi's NTMR Policy is to establish minimum requirements for identifying, measuring, monitoring, controlling, and reporting Non-Trading Market Risk, consistent with Citi’s risk appetite.
The primary purpose of Citi's NTMR Policy is to establish minimum requirements for identifying, measuring, monitoring, controlling, and reporting Non-Trading Market Risk, consistent with Citi’s risk appetite.
That answer is correct.
The primary purpose of Citi's NTMR Policy is to establish minimum requirements for identifying, measuring, monitoring, controlling, and reporting Non-Trading Market Risk, consistent with Citi’s risk appetite.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Non-Trading Market Risk Policy Overview section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Non-Trading Market Risk Policy Overview section.
What are key responsibilities of Board Risk Management Committees (RMCs) as it relates to Non-Trading Market Risk (NTMR)?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The Risk Management Committees (RMCs) are standing committees of the Boards of Directors for Citigroup Inc. and Citibank, N.A. Their responsibilities include:
The Risk Management Committees (RMCs) are standing committees of the Boards of Directors for Citigroup Inc. and Citibank, N.A. Their responsibilities include:
The Risk Management Committees (RMCs) are standing committees of the Boards of Directors for Citigroup Inc. and Citibank, N.A. Their responsibilities include:
That answer is correct.
The Risk Management Committees (RMCs) are standing committees of the Boards of Directors for Citigroup Inc. and Citibank, N.A. Their responsibilities include:
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Governance Structure section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Governance Structure section.
Which phase of the NTMR Lifecycle primarily focuses on:
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The primary focus of the Independent Assurance is creating risk-based assessments to ensure conformance with policies and effectiveness of controls.
The focus of Issue Management is the identification, evaluation, remediation, closure, monitoring, reporting, and escalation of issues related to inadequate risk design or control execution.
The primary focus of the Independent Assurance is creating risk-based assessments to ensure conformance with policies and effectiveness of controls.
The focus of Issue Management is the identification, evaluation, remediation, closure, monitoring, reporting, and escalation of issues related to inadequate risk design or control execution.
The primary focus of the Independent Assurance is creating risk-based assessments to ensure conformance with policies and effectiveness of controls.
The focus of Issue Management is the identification, evaluation, remediation, closure, monitoring, reporting, and escalation of issues related to inadequate risk design or control execution.
That answer is correct.
The primary focus of the Independent Assurance is creating risk-based assessments to ensure conformance with policies and effectiveness of controls.
The focus of Issue Management is the identification, evaluation, remediation, closure, monitoring, reporting, and escalation of issues related to inadequate risk design or control execution.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the NTMR Lifecycle section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the NTMR Lifecycle section.
What is the primary purpose of Management Action Triggers (MATs) in the context of Non-Trading Market Risk?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The primary purpose of MATs is to highlight risk trends and pre-empt limit breaches by triggering escalation and remediation, when exceeded.
The primary purpose of MATs is to highlight risk trends and pre-empt limit breaches by triggering escalation and remediation, when exceeded.
The primary purpose of MATs is to highlight risk trends and pre-empt limit breaches by triggering escalation and remediation, when exceeded.
That answer is correct.
The primary purpose of MATs is to highlight risk trends and pre-empt limit breaches by triggering escalation and remediation, when exceeded.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the NTMR Lifecycle section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the NTMR Lifecycle section.
What is a key objective of the Non-Trading Market Risk Stress Testing Program (STP)?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The key objective of the STP program is to identify, measure, and monitor potential risks coming from interest rate, FX, OCI and other changes across an extensive spectrum of scenarios that may impact the banking book and off-balance sheet items.
The key objective of the STP program is to identify, measure, and monitor potential risks coming from interest rate, FX, OCI and other changes across an extensive spectrum of scenarios that may impact the banking book and off-balance sheet items.
The key objective of the STP program is to identify, measure, and monitor potential risks coming from interest rate, FX, OCI and other changes across an extensive spectrum of scenarios that may impact the banking book and off-balance sheet items.
That answer is correct.
The key objective of the STP program is to identify, measure, and monitor potential risks coming from interest rate, FX, OCI and other changes across an extensive spectrum of scenarios that may impact the banking book and off-balance sheet items.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the NTMR Stress Testing and Models section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the NTMR Stress Testing and Models section.







go to close menu button
go to close button