In this course, you’ll be introduced to EUC Owner Jared and EUC Champion Priya, who will guide you through case studies illustrating the EUC and ITeSS Lifecycle. They’ll collaborate with the following other key team members:



Images of key EUC team members, which include: Jared: EUC Owner, Priya: EUC Champion, Roger: EUC Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate), Karen: Business & Function IT
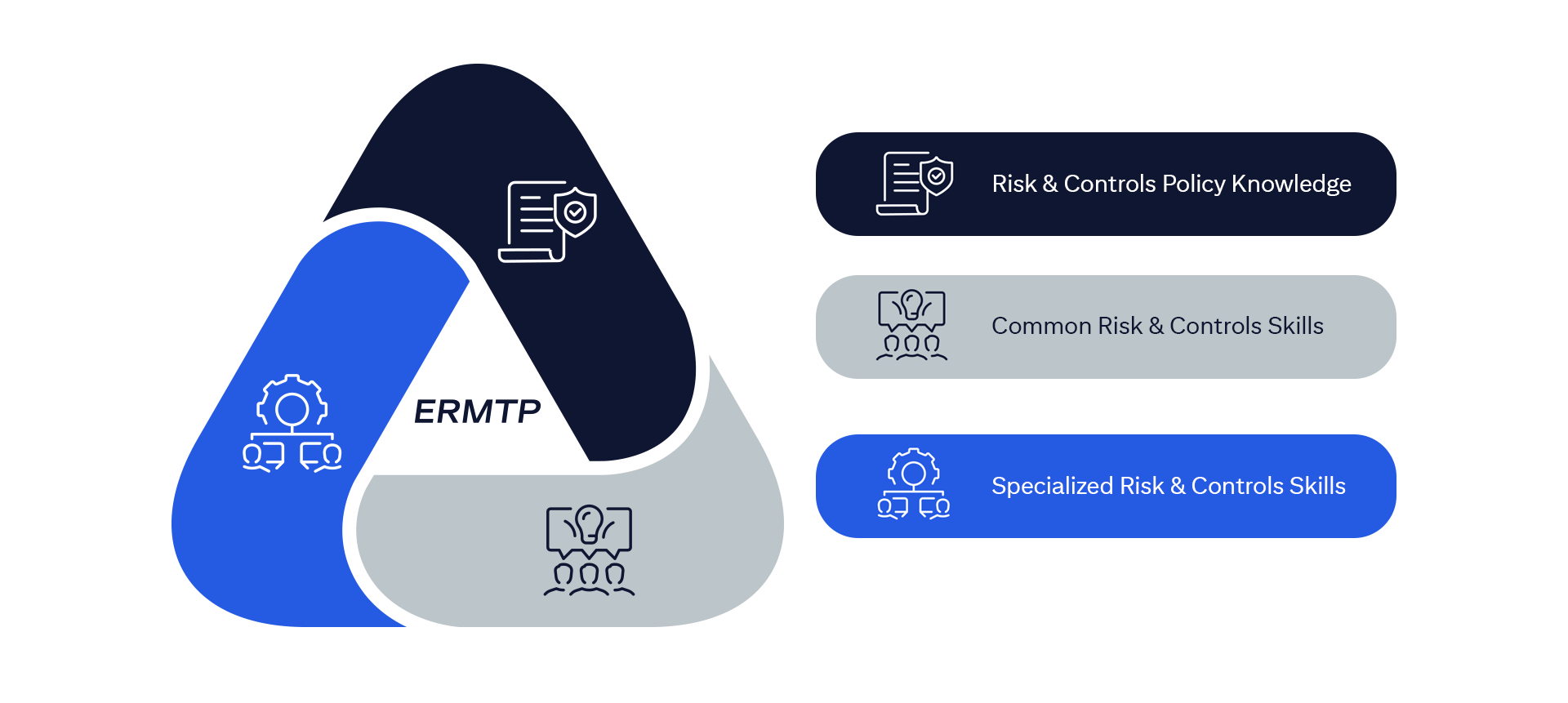
The ERMF establishes an overarching, integrated, and consistent approach to risk management firm wide.
The ERMF has four pillars, as outlined in the following diagram:
Please note: To better understand how Citi manages certain risks, this training will specifically focus on Control within Pillar 3 (Risk Management) of the ERMF. The remaining pillars are addressed in other ERMTP training programs.
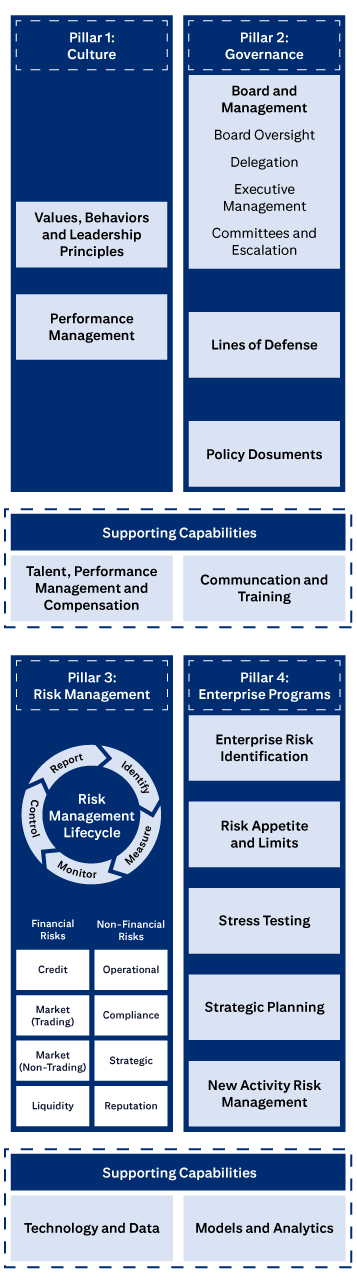
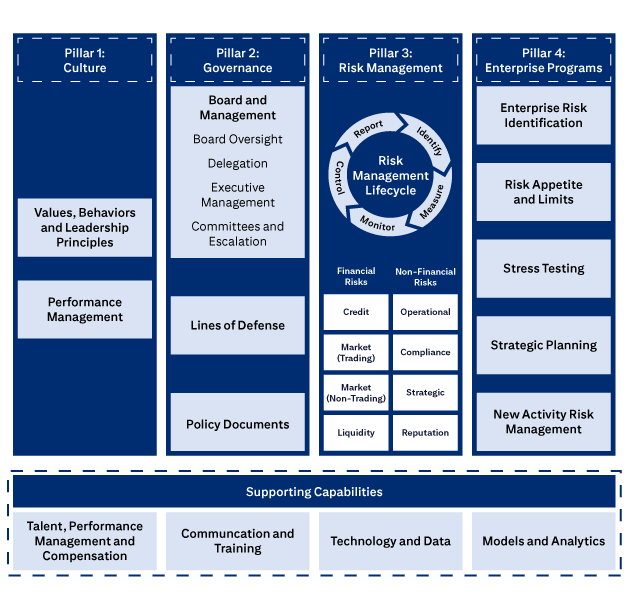

The four pillars of Citi’s ERM Framework.
Pillar 1: Culture includes Values, Behaviors and Leadership Principles, and Performance Management
Pillar 2: Governance includes Board and Management, Board Oversight, Delegation, Executive Management, Committees and Escalation, Lines of Defense, and Policies, Standards and Procedures.
Pillar 3: Risk Management covers the Risk Management Lifecycle (Identify, Measure, Monitor, Control, Report), Financial Risks (Credit, Market (Trading), Market (Non-Trading), Liquidity), and Non-Financial Risks (Operational, Compliance, Strategic, Reputation).
Pillar 4: Enterprise Programs covers Enterprise Risk Identification, Risk Appetite and Limits, Stress Testing, Strategic Planning, and New Activities Approval.
Supporting Capabilities are: Talent, Performance Management and Compensation; Communication and Training; Technology and Data; and Models and Analytics.






The purpose of the Pre-Creation phase is to confirm that an assessment has been performed to evaluate an alternative technology solution prior to creating a new EUC.
To proceed, select each button to learn more about the EUC creation request process.

Evaluation of Alternative Solutions
EUC Owner, Jared, in partnership with Business and Function IT, is responsible for evaluating alternative technology solutions and advising on appropriate technology choices such as:

EUC Creation Request Submission
If an approved IT solution was not available, Jared must submit this request to Roger, his C15+ (or Delegate) for review and approval. Jared may seek guidance from Priya, his EUC Champion, during this process.

EUC Creation Request Approval
EUC Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate), Roger, is responsible for approving EUC creation requests (from Jared, the EUC Owner).
Upon Registration, Jared categorizes the EUC as High Risk due to its impact on financial reporting and potential data integrity issues after completing the initial Risk Assessment.
After the initial risk assessment is approved, there are ongoing monitoring and periodic reassessments triggered by changes. This ensures the EUC's risk level remains current. These reassessments are crucial to account for changes in the EUC's usage, data, or the business environment.
To proceed, select each button to learn more.

The frequency of periodic risk assessments is determined by the EUC's risk level established in the initial assessment. For example:
Due to the high-risk classification of Jared's EUC, he is required to complete the Risk Assessment Questionnaire semi-annually.
go to next button
When material changes are identified during Change Control review, Jared must complete the Risk Assessment within 30 calendar days of the Change Control completion date.
Refer to Risk Assessment Questionnaire in the End User Computing (EUC) Standard document for further information.
go to next button
Jared attests to the accuracy of the Risk Assessment responses and submits the Risk Assessment for approval.
Roger, EUC Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate), reviews and approves the Risk Assessment within the periodic review due date or within 30 calendar days of material change.
Refer to Risk Assessment Questionnaire in the End User Computing (EUC) Standard document for further information.



As you may recall from the foundational course, Jared can reduce reliance on his EUC by using one of the three risk reduction methods.
To proceed, select each method to learn more.
The need for the EUC is eliminated because of a change in the business process(es) resulting from, but not limited to, business transformation, organizational restructuring, process simplification and process optimization.
go to next button
An EUC is eliminated via Migration/Enhancement to Non-ITeSS Technology Platform when the IT system or application is managed by Business and Function IT and the application complies with Citi Information Technology Management Policy (CITMP) and all applicable Citi IT policies.
go to next button
An EUC is eliminated by migrating to an ITeSS where development is guided by Business and Function IT and has a lower risk exposure than an EUC because of increased level of controls.






Several key roles contribute to the successful implementation of ITeSS, as listed here.

Image of Jared: ITeSS Tool Owner
Jared: ITeSS Tool Owner
As you learned earlier, Jared's spreadsheet has been classified as a High Risk EUC. His Risk Reduction plan involves the migration of the EUC functionality to ITeSS. Therefore, Jared has become the ITeSS Tool Owner, and his responsibilities now include:

Image of Roger: ITeSS Tool Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate)
Roger: ITeSS Tool Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate)
As you learned earlier, Roger has approved Jared’s EUC Risk Reduction plan. He continues his role as Jared’s C15+ (or Delegate) and is accountable for the ITeSS Tool. His responsibilities now include:

Image of Priya: EUC Champion
Priya: EUC Champion
As you learned earlier, Priya helped Jared to identify a suitable ITeSS as a potential alternative to the spreadsheet. Her responsibilities now include:

Image of Karen: Business and Function IT
Karen: Business and Function IT

Image of EUC Enterprise Governance Team
EUC Enterprise Governance Team









The first three phases of the EUC Lifecycle are Identification and Pre-Creation, Registration, and Risk Assessment. What are the final two phases?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The five phases of the EUC Lifecycle are: Identification and Pre-Creation, Registration, Risk Assessment, Controls Implementation, and Risk Reduction.
The five phases of the EUC Lifecycle are: Identification and Pre-Creation, Registration, Risk Assessment, Controls Implementation, and Risk Reduction.
The five phases of the EUC Lifecycle are: Identification and Pre-Creation, Registration, Risk Assessment, Controls Implementation, and Risk Reduction.
That answer is correct.
The five phases of the EUC Lifecycle are: Identification and Pre-Creation, Registration, Risk Assessment, Controls Implementation, and Risk Reduction.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the End User Computing (EUC) Lifecycle section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the End User Computing (EUC) Lifecycle section.
Jane, a potential EUC Owner, created a spreadsheet to automate financial reporting. What is the first step she should take in the EUC Lifecycle?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
Before taking any further steps, Jane must confirm that her spreadsheet meets the criteria of an EUC.
Using the spreadsheet before proper registration and Risk Assessment exposes the firm to potential risks.
Submitting a creation request is necessary only for new EUCs. Jane should first confirm if her existing spreadsheet qualifies as an EUC.
Registration is the next step after identifying the spreadsheet as an EUC.
Before taking any further steps, Jane must confirm that her spreadsheet meets the criteria of an EUC.
Using the spreadsheet before proper registration and Risk Assessment exposes the firm to potential risks.
Submitting a creation request is necessary only for new EUCs. Jane should first confirm if her existing spreadsheet qualifies as an EUC.
Registration is the next step after identifying the spreadsheet as an EUC.
Before taking any further steps, Jane must confirm that her spreadsheet meets the criteria of an EUC.
Using the spreadsheet before proper registration and Risk Assessment exposes the firm to potential risks.
Submitting a creation request is necessary only for new EUCs. Jane should first confirm if her existing spreadsheet qualifies as an EUC.
Registration is the next step after identifying the spreadsheet as an EUC.
That answer is correct.
Before taking any further steps, Jane must confirm that her spreadsheet meets the criteria of an EUC.
Using the spreadsheet before proper registration and Risk Assessment exposes the firm to potential risks.
Submitting a creation request is necessary only for new EUCs. Jane should first confirm if her existing spreadsheet qualifies as an EUC.
Registration is the next step after identifying the spreadsheet as an EUC.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the End User Computing (EUC) Lifecycle in Action section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the End User Computing (EUC) Lifecycle in Action section.
You have just received approval to create a new EUC. As the EUC Owner, you’ve already registered the EUC and confirmed the decision tree responses. What are the remaining steps?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
You should first register the EUC, confirm decision tree responses, complete registration fields and initial Risk Assessment, attest accuracy of the information and submit for approval.
You should first register the EUC, confirm decision tree responses, complete registration fields and initial Risk Assessment, attest accuracy of the information and submit for approval.
You should first register the EUC, confirm decision tree responses, complete registration fields and initial Risk Assessment, attest accuracy of the information and submit for approval.
That answer is correct.
You should first register the EUC, confirm decision tree responses, complete registration fields and initial Risk Assessment, attest accuracy of the information and submit for approval.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the End User Computing (EUC) Lifecycle in Action section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the End User Computing (EUC) Lifecycle in Action section.
Who is responsible for supporting and advising the EUC Owner and providing oversight by performing in-business Quality Control (Sector QC) to verify compliance with the EUC Policy?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The EUC Owner and EUC Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate) are involved in quality assurance as a shared responsibility. However, the EUC Champion’s primary role is to support and advise the EUC Owner and to provide oversight by conducting in-business Quality Control (Sector QC) to ensure adherence to EUC Policy.
The EUC Owner and EUC Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate) are involved in quality assurance as a shared responsibility. However, the EUC Champion’s primary role is to support and advise the EUC Owner and to provide oversight by conducting in-business Quality Control (Sector QC) to ensure adherence to EUC Policy.
The EUC Owner and EUC Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate) are involved in quality assurance as a shared responsibility. However, the EUC Champion’s primary role is to support and advise the EUC Owner and to provide oversight by conducting in-business Quality Control (Sector QC) to ensure adherence to EUC Policy.
That answer is correct.
The EUC Owner and EUC Owner’s C15+ (or Delegate) are involved in quality assurance as a shared responsibility. However, the EUC Champion’s primary role is to support and advise the EUC Owner and to provide oversight by conducting in-business Quality Control (Sector QC) to ensure adherence to EUC Policy.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Quality Control and Assurance Review and Effectiveness section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Quality Control and Assurance Review and Effectiveness section.
What is required of an EUC Owner after a Critical or High Risk Assessment rating is approved?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
For EUCs rated Critical or High, the EUC Owner must develop and submit a Risk Reduction Plan and obtain approval within 90 calendar days. Medium-risk EUCs only require a plan if included in the Annual Risk Reduction Commitment.
For EUCs rated Critical or High, the EUC Owner must develop and submit a Risk Reduction Plan and obtain approval within 90 calendar days. Medium-risk EUCs only require a plan if included in the Annual Risk Reduction Commitment.
For EUCs rated Critical or High, the EUC Owner must develop and submit a Risk Reduction Plan and obtain approval within 90 calendar days. Medium-risk EUCs only require a plan if included in the Annual Risk Reduction Commitment.
That answer is correct.
For EUCs rated Critical or High, the EUC Owner must develop and submit a Risk Reduction Plan and obtain approval within 90 calendar days. Medium-risk EUCs only require a plan if included in the Annual Risk Reduction Commitment.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Risk Reduction section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Risk Reduction section.
Business has decided to migrate a Critical Risk to a Non-ITeSS Technology Platform. However, the migration will take 2 years to complete.
What is the Business team’s best solution?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
EUCs assessed as Critical must migrate within 12 months, and High-Risk EUCs within 18 months. If migration isn’t possible within this timeframe, a Risk Reduction plan using an ITeSS Tool must be implemented.
EUCs assessed as Critical must migrate within 12 months, and High-Risk EUCs within 18 months. If migration isn’t possible within this timeframe, a Risk Reduction plan using an ITeSS Tool must be implemented.
EUCs assessed as Critical must migrate within 12 months, and High-Risk EUCs within 18 months. If migration isn’t possible within this timeframe, a Risk Reduction plan using an ITeSS Tool must be implemented.
That answer is correct.
EUCs assessed as Critical must migrate within 12 months, and High-Risk EUCs within 18 months. If migration isn’t possible within this timeframe, a Risk Reduction plan using an ITeSS Tool must be implemented.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Risk Reduction section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the Risk Reduction section.
Which phase of the ITeSS Lifecycle involves monitoring and maintaining the Tool in the production environment?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The Operate and Implement Controls phase focuses on monitoring, managing, and maintaining the ITeSS Tool in the production environment to ensure it continues to function securely and effectively.
The Operate and Implement Controls phase focuses on monitoring, managing, and maintaining the ITeSS Tool in the production environment to ensure it continues to function securely and effectively.
The Operate and Implement Controls phase focuses on monitoring, managing, and maintaining the ITeSS Tool in the production environment to ensure it continues to function securely and effectively.
That answer is correct.
The Operate and Implement Controls phase focuses on monitoring, managing, and maintaining the ITeSS Tool in the production environment to ensure it continues to function securely and effectively.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the ITeSS Lifecycle in Action section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the ITeSS Lifecycle in Action section.
What is the primary responsibility of the Business and Function IT during the Opportunity Identification phase of the ITeSS Lifecycle?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The Business and Function IT helps the ITeSS Tool Owner identify a platform by considering factors like data security and compliance in the Opportunity Identification phase.
Approving the budget for the ITeSS Tool is typically the responsibility of the C15+ (or Delegate). Developing the initial design of the ITeSS Tool is done in the Define and Design step, often collaboratively with the Business and Function IT.
Deploying the ITeSS Tool to the production environment is typically done by the Business and Function IT in coordination with the C15+ (or Delegate) in Testing and Deployment Phase.
The Business and Function IT helps the ITeSS Tool Owner identify a platform by considering factors like data security and compliance in the Opportunity Identification phase.
Approving the budget for the ITeSS Tool is typically the responsibility of the C15+ (or Delegate). Developing the initial design of the ITeSS Tool is done in the Define and Design step, often collaboratively with the Business and Function IT.
Deploying the ITeSS Tool to the production environment is typically done by the Business and Function IT in coordination with the C15+ (or Delegate) in Testing and Deployment Phase.
The Business and Function IT helps the ITeSS Tool Owner identify a platform by considering factors like data security and compliance in the Opportunity Identification phase.
Approving the budget for the ITeSS Tool is typically the responsibility of the C15+ (or Delegate). Developing the initial design of the ITeSS Tool is done in the Define and Design step, often collaboratively with the Business and Function IT.
Deploying the ITeSS Tool to the production environment is typically done by the Business and Function IT in coordination with the C15+ (or Delegate) in Testing and Deployment Phase.
That answer is correct.
The Business and Function IT helps the ITeSS Tool Owner identify a platform by considering factors like data security and compliance in the Opportunity Identification phase.
Approving the budget for the ITeSS Tool is typically the responsibility of the C15+ (or Delegate). Developing the initial design of the ITeSS Tool is done in the Define and Design step, often collaboratively with the Business and Function IT.
Deploying the ITeSS Tool to the production environment is typically done by the Business and Function IT in coordination with the C15+ (or Delegate) in Testing and Deployment Phase.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the ITeSS Lifecycle in Action section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the ITeSS Lifecycle in Action section.
Who is responsible for identifying the need for an ITeSS Tool in the case study?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
The ITeSS Tool Owner identifies the need to automate a complex financial reporting process.
The EUC Champion helps Jared identify a suitable platform, but Jared himself recognizes the need.
The Business & Function IT is involved in the development, deployment, and maintenance of ITeSS Tools.
The C15+ (or Delegate) confirms that existing Non-ITeSS Technology Platform applications cannot fulfill the requirement.
The ITeSS Tool Owner identifies the need to automate a complex financial reporting process.
The EUC Champion helps Jared identify a suitable platform, but Jared himself recognizes the need.
The Business & Function IT is involved in the development, deployment, and maintenance of ITeSS Tools.
The C15+ (or Delegate) confirms that existing Non-ITeSS Technology Platform applications cannot fulfill the requirement.
The ITeSS Tool Owner identifies the need to automate a complex financial reporting process.
The EUC Champion helps Jared identify a suitable platform, but Jared himself recognizes the need.
The Business & Function IT is involved in the development, deployment, and maintenance of ITeSS Tools.
The C15+ (or Delegate) confirms that existing Non-ITeSS Technology Platform applications cannot fulfill the requirement.
That answer is correct.
The ITeSS Tool Owner identifies the need to automate a complex financial reporting process.
The EUC Champion helps Jared identify a suitable platform, but Jared himself recognizes the need.
The Business & Function IT is involved in the development, deployment, and maintenance of ITeSS Tools.
The C15+ (or Delegate) confirms that existing Non-ITeSS Technology Platform applications cannot fulfill the requirement.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the ITeSS Lifecycle in Action section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the ITeSS Lifecycle in Action section.
Ricardo is transitioning a High Risk database EUC to an ITeSS Platform. He works with his Business and Function IT to define the scope of the solution and identify impacted stakeholders.
What should Ricardo do next in the Define and Design phase?
Select the best response from the four options and then select Submit.
Please use the Space key only when selecting a radio option with the keyboard. The Enter key is not fully supported. If the Enter key has been used to select a radio option, please use the Escape key. Then you will be able to use the Space key again to select a radio option.
His next step is to document the requirements, including data sources, then process workflows, and document critical success factors. Key Stakeholders will then review and approve the design, ensuring it aligns with business needs and Citi's IT policies.
His next step is to document the requirements, including data sources, then process workflows, and document critical success factors. Key Stakeholders will then review and approve the design, ensuring it aligns with business needs and Citi's IT policies.
His next step is to document the requirements, including data sources, then process workflows, and document critical success factors. Key Stakeholders will then review and approve the design, ensuring it aligns with business needs and Citi's IT policies.
That answer is correct.
His next step is to document the requirements, including data sources, then process workflows, and document critical success factors. Key Stakeholders will then review and approve the design, ensuring it aligns with business needs and Citi's IT policies.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the ITeSS Lifecycle in Action section.
That answer is not correct.
Refer to the ITeSS Lifecycle in Action section.









go to close menu button
go to close button